Research Overview
Research at Energy, Environment and Exposure Laboratory (EEEL) focuses on various aspects of energy, environment, and human exposure. Since the energy, environment, and human exposure are not independent, we aim to understand their complex interdependency. Some of the currently active research themes at EEEL are listed below. Some of these projects are interconnected but are listed as separate projects for the ease of your reference.
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
In India and potentially in other developing nations, time spent by us in built environments such as homes, offices, and classrooms is increasing with urbanization and change in our lifestyle. Therefore, the exposure to airborne pollutants occurring in indoor spaces could be comparable or even exceed that occurring while outdoors. However, outdoor or ambient outdoor pollution is most talked about by researchers, the general public, media, regulators, and policymakers. The critical knowledge gaps we are trying to fill are:
- The current status of indoor air quality in a range of built environments in urban India.
- Pollutant source characterization.
- Transport, transformation, and the fate of pollutants.
- Nexus between IAQ and design and operating features of built environments.

Airborne Transmission of Pathogens such as Coronavirus
With the ongoing COVID pandemics, the research on the airborne transmission of disease-causing pathogens has gained impetus. The probability of catching an infection is much higher in an indoor space because these airborne pathogens can linger on in indoor air within our proximity for a longer time relative to outdoors. Therefore, it is critical to understand the dynamics of airborne pathogens in indoor spaces to develop and implement mitigation strategies. The research at EEEL uses both experimental data and results from computational fluid dynamics simulations to assess how resistants are different built environments against the spread of coronavirus.
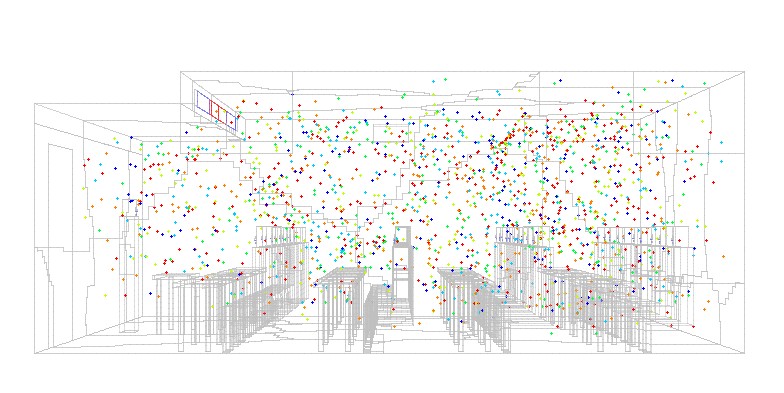
Green Buildings
HVAC systems, maintaining the occupants’ thermal comfort, usually account for the largest chunk of a building’s energy consumption. Operating these HVAC systems also to maintain good air quality can further increase energy consumption. The new building construction rate in India is among the highest globally, presenting a timely opportunity to develop strategies and technologies to tackle indoor air pollution while minimizing energy consumption. Another aspect is green building certifications which currently focus on energy and sustainability with little to no weightage to indoor air quality. There will always be a trade-off between indoor air quality and energy consumption. However, the existing building rating processes are yet to recognize and account for these trade-offs.
Modeling of Residential Scale Solar Energy Systems
Roof-top or residential-scale solar panels can significantly increase the share of renewable energy in a nation’s energy portfolio. However, the roof-top solar energy generation systems yet to achieve full potential in India. The low adoption is due to a complex interplay between policies, regulations, economics, technology, user awareness, and reliability. The current research at EEEL aims to develop a holistic understanding of technological, economic, regulatory, and societal aspects to enable the mass adoption of roof-top solar energy generation systems. We anticipate applying some insights to understand the adoption of other new technologies, such as replacing LPG or PNG stoves with induction stoves.
Funding
Ongoing projects:
1. “Investigating Air Quality and its Dynamics in Built Environments in Urban India” (2022-2024). Funding Agency: SERB DST
2. “Assessing the exposure to airborne pollutants and risk of airborne transmission of pathogens in built environments” (2021-2022). Funding Agency: IIT Gandhinagar
